
购买的OLED
芯片:SS1306
接口:I2C
分辨率:128x32
尺寸:0.91
管脚:4针
电压:3.3V

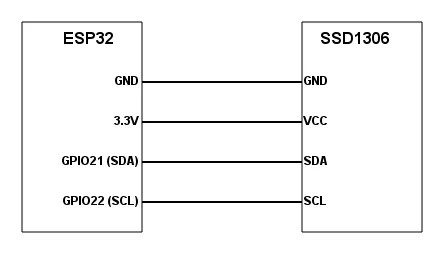
接口定义: GND VCC SCK 串行时钟输入 SDA 串行数据
按如图连接
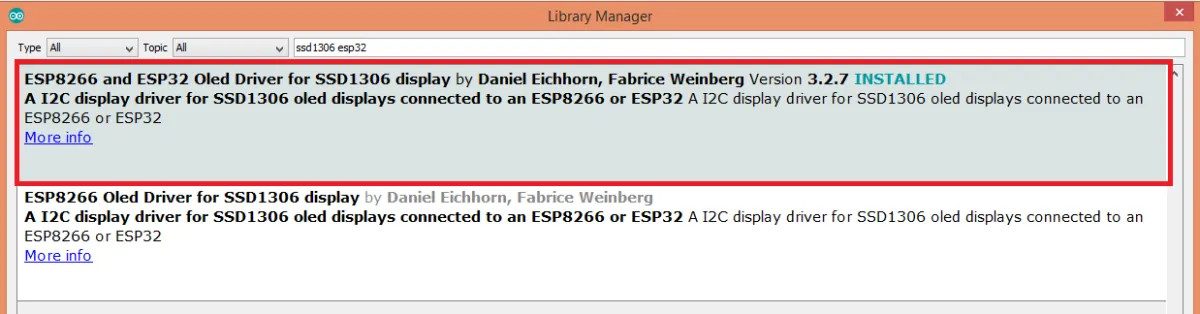
在arduino中,直接下载库就可以使用
导入库 #include “SSD1306.h”
SSD1306 display(0x3c, 21, 22); //ssd1603默认地址是0x3c,21/22作为数据和时钟。 //ESP32的I2C默认 22SCL,21SDA //ESP8266默认 5SCL,4SDA
display.init(); //初始化
display.setFont(ArialMT_Plain_24); //不指定字体时,我看不出它显示的啥
display.drawString(0, 0, “Hello World”);
display.display(); //显示出内容
整个测试代码还是相当简单,但没有找到自己匹配资源之前,也是两眼抓瞎。
有实现基本的驱动之后,接下来就可以看看库,考虑如何实现中文显示等。
看到另一个例子中提到过I2C可以使用任意端口,这篇网文中使用了14/15,有机会也可以试试。只需要 SSD1306 display(0x3c, 15, 14);
当不确定地址时,可以用以下程序扫描
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial);
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop() {
int nDevices = 0;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
for (byte address = 1; address < 127; ++address) {
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
byte error = Wire.endTransmission();
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address < 16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.print(address, HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
++nDevices;
} else if (error == 4) {
Serial.print("Unknown error at address 0x");
if (address < 16) {
Serial.print("0");
}
Serial.println(address, HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0) {
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
} else {
Serial.println("done\n");
}
delay(5000); // Wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
以下示例是显示动态几何图形,感觉频率还是可以的
#include "SSD1306.h"
SSD1306 display(0x3c, 21, 22);
int nFrames = 36;
void HariChord(int frame)
{
display.clear();
int n = 7;
int r = frame * 64 / nFrames;
float rot = frame * 2*PI / nFrames;
for (int i=0; i<(n-1); i++) {
float a = rot + i * 2*PI / n;
int x1 = 64 + cos(a) * r;
int y1 = 32 + sin(a) * r;
for (int j=i+1; j<n; j++) {
a = rot + j * 2*PI / n;
int x2 = 64 + cos(a) * r;
int y2 = 32 + sin(a) * r;
display.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
}
display.display();
}
void setup() {
display.init();
display.clear();
display.setBrightness(10);
display.setColor(WHITE); //字体颜色
display.display();
}
void loop() {
//这里实现了放大了缩小显示
for (int frame=0; frame < nFrames; frame++) {
HariChord(frame);
}
for (int frame=(nFrames-1); frame >= 0; frame--) {
HariChord(frame);
}
}

 打赏
打赏